Free printable PDF lesson plans, word banks, quizzes and games for EFL/ESL teachers
ADVANCED LISTENING PRACTICE
GLOBAL POPULATION
GLOBAL POPULATION
Audio Script
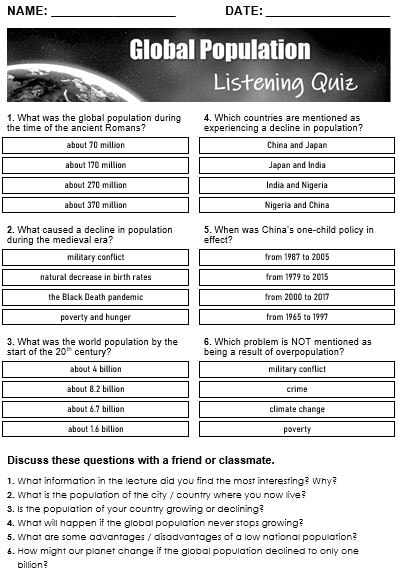
What does global population mean? Global population means the total number of people alive in the world. During the past two millennia, there have been some astonishing changes in world population. About 2000 years ago, during the Roman era, the world population is estimated to have been approximately 170 million people.
Then, about 700 years ago, there was a massive population decline caused by the Black Death in medieval Europe. As much as one-half of the European population died from the disease. However, by the late fourteenth century, global population trends had reversed and once again continued to move upwards; the world population at that time was about 370 million people.
By the 19th century, the Industrial Revolution led to a massive surge in population growth in Europe and North America, with the global population reaching around 1.6 billion by 1900. This growth continued into the 20th century, with the global population reaching 6 billion by the year 2000.
According to the United Nations, the world's population is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, up from 8 billion in 2023. This population growth is mainly due to the high birth rates in developing countries, particularly in Africa and Asia. One notable example is India. India is projected to soon surpass China as the world's most populous country by 2027, and its population is expected to reach 1.64 billion by 2050. Nigeria is another country where the population is projected to increase rapidly, and it is expected to become the world's third most populous country by 2050.
While overpopulation is a serious issue in most countries of the world, current trends suggest that the global population growth rate may decrease in the coming decades. Japan and China are examples of countries where the population is now in decline. Japan has the world's highest percentage of elderly people, and, due to its very low birth rate, its population is projected to drop from its current estimate of 126 million to around 88 million by 2065. China's population is also expected to decrease due to its one-child policy, which was in place from 1979 to 2015. Although the policy is no longer in effect, many Chinese couples continue to have only one child.
Nevertheless, overpopulation, even if limited to only certain parts of the world, can have severe consequences for all of us alive today. It puts a strain on the planet's resources, including food, water, and energy. It can also lead to environmental degradation, such as deforestation and habitat destruction, military conflict, and even contribute to climate change. Furthermore, overpopulation can lead to social and economic problems, such as overcrowding, poverty, and inequality. It is essential, therefore, to address the issue of overpopulation to ensure a sustainable future for the planet and all of its inhabitants.
What does global population mean? Global population means the total number of people alive in the world. During the past two millennia, there have been some astonishing changes in world population. About 2000 years ago, during the Roman era, the world population is estimated to have been approximately 170 million people.
Then, about 700 years ago, there was a massive population decline caused by the Black Death in medieval Europe. As much as one-half of the European population died from the disease. However, by the late fourteenth century, global population trends had reversed and once again continued to move upwards; the world population at that time was about 370 million people.
By the 19th century, the Industrial Revolution led to a massive surge in population growth in Europe and North America, with the global population reaching around 1.6 billion by 1900. This growth continued into the 20th century, with the global population reaching 6 billion by the year 2000.
According to the United Nations, the world's population is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, up from 8 billion in 2023. This population growth is mainly due to the high birth rates in developing countries, particularly in Africa and Asia. One notable example is India. India is projected to soon surpass China as the world's most populous country by 2027, and its population is expected to reach 1.64 billion by 2050. Nigeria is another country where the population is projected to increase rapidly, and it is expected to become the world's third most populous country by 2050.
While overpopulation is a serious issue in most countries of the world, current trends suggest that the global population growth rate may decrease in the coming decades. Japan and China are examples of countries where the population is now in decline. Japan has the world's highest percentage of elderly people, and, due to its very low birth rate, its population is projected to drop from its current estimate of 126 million to around 88 million by 2065. China's population is also expected to decrease due to its one-child policy, which was in place from 1979 to 2015. Although the policy is no longer in effect, many Chinese couples continue to have only one child.
Nevertheless, overpopulation, even if limited to only certain parts of the world, can have severe consequences for all of us alive today. It puts a strain on the planet's resources, including food, water, and energy. It can also lead to environmental degradation, such as deforestation and habitat destruction, military conflict, and even contribute to climate change. Furthermore, overpopulation can lead to social and economic problems, such as overcrowding, poverty, and inequality. It is essential, therefore, to address the issue of overpopulation to ensure a sustainable future for the planet and all of its inhabitants.